Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common and potentially serious health issue, particularly among the elderly. As people age, changes in the body and immune system make older adults more susceptible to infections, including UTIs. Recognizing the unique symptoms, causes, and risk factors in elderly patients is essential for early diagnosis and effective treatment. Untreated UTIs can lead to severe complications, such as kidney infections or sepsis, making prompt medical attention crucial. This article provides an in-depth look at UTIs in the elderly, covering prevention strategies, treatment options, and the role of caregivers in managing these infections. Understanding how to prevent and treat UTIs can improve overall health and quality of life for older adults.
Discover more about this topic with ujocis.net in detail.
1. Overview of Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) occur when harmful bacteria, typically from the gastrointestinal tract, enter the urinary system. The infection can affect any part of the urinary tract, including the urethra, bladder, ureters, or kidneys. While UTIs are common across all age groups, they are especially prevalent in the elderly due to factors such as weakened immune function, decreased mobility, and changes in the urinary system related to aging.
UTIs can be categorized as either lower urinary tract infections, affecting the bladder and urethra, or upper urinary tract infections, which involve the kidneys. In elderly patients, the symptoms of UTIs may differ from younger individuals, often presenting as confusion, fatigue, or general malaise rather than the typical signs like painful urination or a strong urge to urinate. This can make UTIs more difficult to detect and treat in a timely manner.
Complications of untreated UTIs, particularly in older adults, can be serious and include kidney damage, recurring infections, and sepsis. As a result, understanding the nature of UTIs, how they develop, and their impact on elderly individuals is critical to effective management. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to preventing further complications and maintaining the health and well-being of the aging population.

2. Common Causes of UTIs in the Elderly
An elderly woman, seated in a comfortable home environment, appears slightly fatigued and confused, subtly reflecting the common symptoms of a urinary tract infection in older adults. She is wearing a cozy cardigan and glasses, with a gentle expression, conveying vulnerability but also resilience. The background includes soft lighting and a cup of tea on a table nearby, symbolizing care and comfort. Her posture and facial expression suggest she is being mindful of her health, possibly feeling discomfort, but still engaged in her surroundings.

3. Risk Factors Specific to Older Adults
An elderly woman, seated in a comfortable home environment, appears slightly fatigued and confused, subtly reflecting the common symptoms of a urinary tract infection in older adults. She is wearing a cozy cardigan and glasses, with a gentle expression, conveying vulnerability but also resilience. The background includes soft lighting and a cup of tea on a table nearby, symbolizing care and comfort. Her posture and facial expression suggest she is being mindful of her health, possibly feeling discomfort, but still engaged in her surroundings.
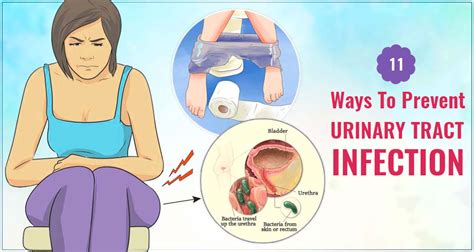
4. Symptoms of UTIs in Elderly Patients
An elderly woman, seated in a comfortable home environment, appears slightly fatigued and confused, subtly reflecting the common symptoms of a urinary tract infection in older adults. She is wearing a cozy cardigan and glasses, with a gentle expression, conveying vulnerability but also resilience. The background includes soft lighting and a cup of tea on a table nearby, symbolizing care and comfort. Her posture and facial expression suggest she is being mindful of her health, possibly feeling discomfort, but still engaged in her surroundings.
5. Complications of Untreated UTIs in the Elderly
An elderly woman, seated in a comfortable home environment, appears slightly fatigued and confused, subtly reflecting the common symptoms of a urinary tract infection in older adults. She is wearing a cozy cardigan and glasses, with a gentle expression, conveying vulnerability but also resilience. The background includes soft lighting and a cup of tea on a table nearby, symbolizing care and comfort. Her posture and facial expression suggest she is being mindful of her health, possibly feeling discomfort, but still engaged in her surroundings.
6. Diagnostic Procedures for UTIs
An elderly woman, seated in a comfortable home environment, appears slightly fatigued and confused, subtly reflecting the common symptoms of a urinary tract infection in older adults. She is wearing a cozy cardigan and glasses, with a gentle expression, conveying vulnerability but also resilience. The background includes soft lighting and a cup of tea on a table nearby, symbolizing care and comfort. Her posture and facial expression suggest she is being mindful of her health, possibly feeling discomfort, but still engaged in her surroundings.
7. Effective Treatment Options
An elderly woman, seated in a comfortable home environment, appears slightly fatigued and confused, subtly reflecting the common symptoms of a urinary tract infection in older adults. She is wearing a cozy cardigan and glasses, with a gentle expression, conveying vulnerability but also resilience. The background includes soft lighting and a cup of tea on a table nearby, symbolizing care and comfort. Her posture and facial expression suggest she is being mindful of her health, possibly feeling discomfort, but still engaged in her surroundings.
8. Prevention Strategies for Reducing UTI Risk
An elderly woman, seated in a comfortable home environment, appears slightly fatigued and confused, subtly reflecting the common symptoms of a urinary tract infection in older adults. She is wearing a cozy cardigan and glasses, with a gentle expression, conveying vulnerability but also resilience. The background includes soft lighting and a cup of tea on a table nearby, symbolizing care and comfort. Her posture and facial expression suggest she is being mindful of her health, possibly feeling discomfort, but still engaged in her surroundings.
9. Role of Caregivers in Managing UTIs
An elderly woman, seated in a comfortable home environment, appears slightly fatigued and confused, subtly reflecting the common symptoms of a urinary tract infection in older adults. She is wearing a cozy cardigan and glasses, with a gentle expression, conveying vulnerability but also resilience. The background includes soft lighting and a cup of tea on a table nearby, symbolizing care and comfort. Her posture and facial expression suggest she is being mindful of her health, possibly feeling discomfort, but still engaged in her surroundings.
10. Long-term Management and Monitoring
An elderly woman, seated in a comfortable home environment, appears slightly fatigued and confused, subtly reflecting the common symptoms of a urinary tract infection in older adults. She is wearing a cozy cardigan and glasses, with a gentle expression, conveying vulnerability but also resilience. The background includes soft lighting and a cup of tea on a table nearby, symbolizing care and comfort. Her posture and facial expression suggest she is being mindful of her health, possibly feeling discomfort, but still engaged in her surroundings.
An elderly woman, seated in a comfortable home environment, appears slightly fatigued and confused, subtly reflecting the common symptoms of a urinary tract infection in older adults. She is wearing a cozy cardigan and glasses, with a gentle expression, conveying vulnerability but also resilience. The background includes soft lighting and a cup of tea on a table nearby, symbolizing care and comfort. Her posture and facial expression suggest she is being mindful of her health, possibly feeling discomfort, but still engaged in her surroundings.
ujocis.net

